


The sliding action of polar microtubules exerts a pressure that drive the poles apart. Here, motor proteins at the center, push the poles apart and those at poles, pull the poles apart.Īstral microtubules directly act on respective poles to move them apart. Sister chromosomes now start moving to opposite poles. Here, tubulin protein is gradually removed. For this, the kinetochore starts to contract or shorten. In anaphase stage, the kinetochore microtubule pull the two sister chromatids toward opposite poles. These factors eventually arrange the chromosomes in the metaphase plate. There are also some microtubule-dependent motor proteins viz. The + end of the microtubule associate with the kinetochore. As they elongate, they find the centromere of the chromosome. Microtubules add tubulin proteins to elongate across the cell. This will not happen until chromosomes and spindle fibers find each other inside the cell. The main purpose of spindle fibers is to move the chromosomes equally into two daughter cells. The microtubules attach to the kinetochore and stabilize to form kinetochore microtubules. This serves as an attachment site for microtubules. Kinetochore is present inside the centromere. Kinetochore microtubule – The two arms of chromosomes remain associated at a point called the centromere. Polar microtubule – These microtubules do not interact with chromosomes. Plant cells lack astral microtubules as they lack centrosome.
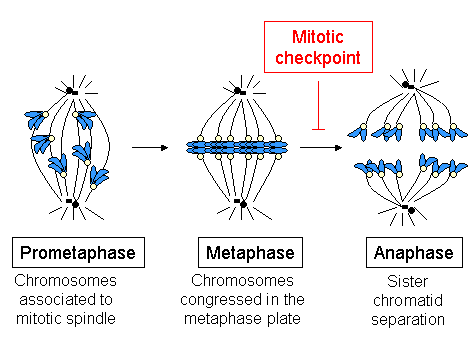
These astral microtubules move out from the centrosome towards the cell. They are astral, polar and kinetochore microtubules.Īstral microtubules – Each centrosome at the opposite poles form a radial array of microtubules called the aster. Spindle fibers are of three types based on their formation inside the cell. Overall, the spindle fibers have there “–“ end in the centrosome and the “+” end point outwards. For microtubules the “+” end lies away from spindle pole and “–“ end is embedded in spindle pole. For centrioles, the “+” end is in MTOC and “–“ end is away from it. It means that they have a positive (+) end and a negative (–) end. Spindle fibers is a combination of microtubules and centriole, both of which are polarized structures. In higher plant cells, MTOC do not have centrioles but they still form spindle fibers. Overall, it becomes a shape of spindle, which is broader in middle and tapers at opposite ends, which gives rise to cell poles. Each centrosome now form a radial array of microtubules in all positions. They position themselves at opposite poles of the cell. As the M phase begins, the two pair of centrioles separate. The two centriole pairs remain together until the start of Mitosis phase or M phase. It duplicates in the interphase stage of the cell cycle as the amount of DNA also doubles. Most animal cells have a single centrosome. In animal cells, an MTOC with a pair of centrioles is called the centrosome. A centriole is a barrel shaped structure made of microtubules. In animal cells, this MTOC has a pair of centrioles. The subunit of a microtubule is alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin. Microtubules in a cell are arranged at the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC). The spindle fibers are formed from the centrosome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
